Open data - Download the Knowledge base
You are free to download the data of this Knowledge base.
To do this you must be an authenticated user: log in or sign in now.
All the data are licensed as Creative Common CC-BY 4.0.
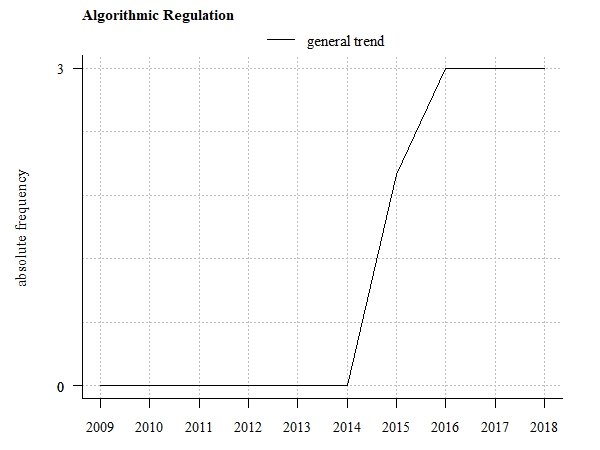
This trend deals with the use of algorithms in policy and decision making. First, there is the trend of algorithmic regulation. Algorithmic regulation means that regulatory decision making is delegated to algorithms. The algorithms give the instructions of what should be done to achieve a desired outcome. [1]
The trend of using algorithms in governance and an increasing reliance of public decision making on algorithms is sometimes also called algocracy. [2]
In this context two other more ideological and sceptical terms has been raised. Dataism is a kind of ideology or philosophy in which trusts in Big Data and algorithms is central and which relies on the assumption, that the world´s complexity can be handled through data. Yuval Harari introduced this ideology in his book “Homo Deus” to a wider audience. Dataism is very similar to the obove mentioned trend of algorithmic accountability/ algogracy. [3] [4]
Solutionism is a term coined by Evgeny Morozov. Solutionism means the belief that there are simple technical solutions to everything. It´s about the conviction that technologies, algorithms and robots can solve highly complex social problems by making processes more efficient. Morozov is critical of such an ideology of problem solving, in which algorithms and not elected governments make the decision. [5] [6]
Algorithmic Regulation is further accompanied by algorithmic accountability. Algorithmic Accountability concerns control mechanisms of the algorithms used for decision making. It has emerged as a concept in the public and private sector that includes obligations through which algorithmic decision making needs to be reported, explained and justified, to mitigate any negative social impacts, biases or potential harms. The goal is to hold the algorithmic regulation accountable and ensure transparency in algorithm-based decision making processes. [7]
| Agenda Setting | Policy Design and Analysis | Policy Implementation | Policy Monitoring and Evaluation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture, Fisheries, Forestry & Foods | ||||
| Economy & Finance | ||||
| Education, Youth, Culture & Sport | ||||
| Employment & Social Security | ||||
| Environment & Energy | ||||
| Health | ||||
| Foreign Affairs and Defence | ||||
| Justice, Legal System & Public Safety | ||||
| Public Affairs | ||||
| Innovation, Science & Technology | ||||
| Urban Planning & Transport | ||||
| Institutional Questions / Internal Affairs |
You are free to download the data of this Knowledge base.
To do this you must be an authenticated user: log in or sign in now.
All the data are licensed as Creative Common CC-BY 4.0.