Open data - Download the Knowledge base
You are free to download the data of this Knowledge base.
To do this you must be an authenticated user: log in or sign in now.
All the data are licensed as Creative Common CC-BY 4.0.
The pressure to redesign city infrastructures is strong, since climate change and the problem of allocation are defining new requirements, which will not be met through cosmetic and maintenance repairs. In particular, energy infrastructures like water, waste or recycling are affected by this issue.
The following description draws a picture for future smart cities.
Innovative infrastructures will be characterised through digital management systems based on real time data processing. Infrastructure components and communal rooms are interconnected due to innovative communications systems. Decentralised systems are connected with central networks and buildings will produce energy as decentralised energy providers. Traffic will be resource saving through emission-free individual, economical and public transport and new mobility concepts will be established. The public administration will be evolved to an open government, which provides open data and services and develops new governance structures with respect to participative communications, stable health care structures and public safety strategies. [1]
The European Innovation Partnership on Smart Cities and Communities has identified the need for an approach of more integrated infrastructures, which have led to the creation of a reference architecture with the view to provide a vendor agnostic, interoperable, and standards-based orientation for an open urban platform to cities and communities. [2]
In a broader context, the term Smart Government has been arisen to address not only the local level, but rather all levels of government. In accordance to smart cities, it addresses an intelligently networked governance, which uses the opportunities of interconnected smart objects and cyber physical systems for the efficient and effective performance of public tasks. [3]
| Agenda Setting | Policy Design and Analysis | Policy Implementation | Policy Monitoring and Evaluation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture, Fisheries, Forestry & Foods | ||||
| Health | ||||
| Foreign Affairs and Defence | ||||
| Education, Youth, Culture & Sport | ||||
| Employment & Social Security | ||||
| Environment & Energy | ||||
| Health | ||||
| Foreign Affairs and Defence | ||||
| Justice, Legal System & Public Safety | ||||
| Public Affairs | ||||
| Innovation, Science & Technology | ||||
| Urban Planning & Transport | ||||
| Institutional Questions / Internal Affairs |
You are free to download the data of this Knowledge base.
To do this you must be an authenticated user: log in or sign in now.
All the data are licensed as Creative Common CC-BY 4.0.
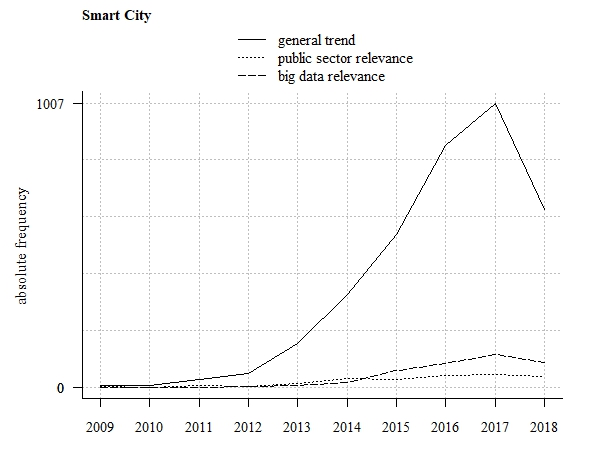
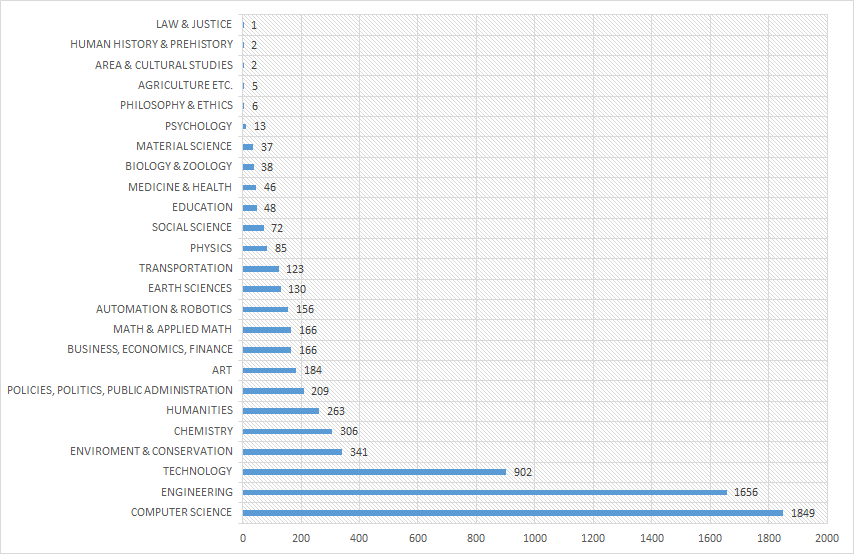
Smart Cities
Smart Cities are indeed a trending topic, particularly around the EU. The analysis conducted is of real added value! The part where you show the list of assets that can address or materialize the trend is the ultimate starting point for anyone that wants to process how the concept of a smart city can be brought to life!