Open data - Download the Knowledge base
You are free to download the data of this Knowledge base.
To do this you must be an authenticated user: log in or sign in now.
All the data are licensed as Creative Common CC-BY 4.0.
New technologies have great influence on work and work processes, as we know them today. For example, new technologies offer the possibility of mobile work, can optimise the work process and make it more economical. [1]
Smartness means in this context, that work is connected to innovations, sustainability, and competitiveness. Smart Work is based on the recognition that the working environment must be redesigned due to an increasing digitisation. This reorganisation of the work is associated to the use of technologies, for example, mobile devices, which allow employees to work anytime and anywhere and makes the work more flexible and innovative. Advantages of this smartness are, for example, time saving, improved work-life balance, increased productivity, and in consequence better performance. The public service is not excluded from this developments – it is also facing a profound change and must find new ways to create an attractive work environment.
As Eom et al. stated, smart work is a fundamental part of smart government and contributes to the government’s efficiency. [2]
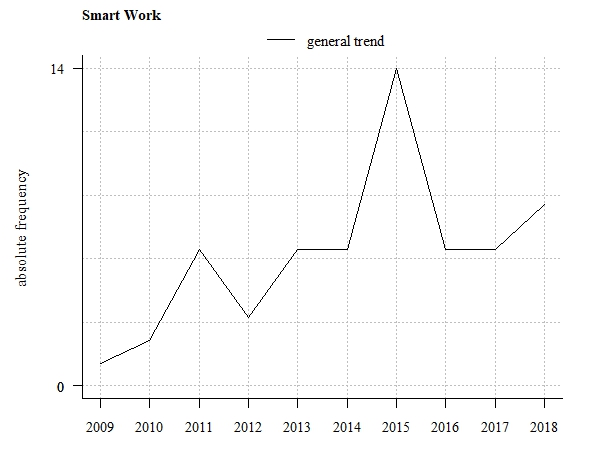
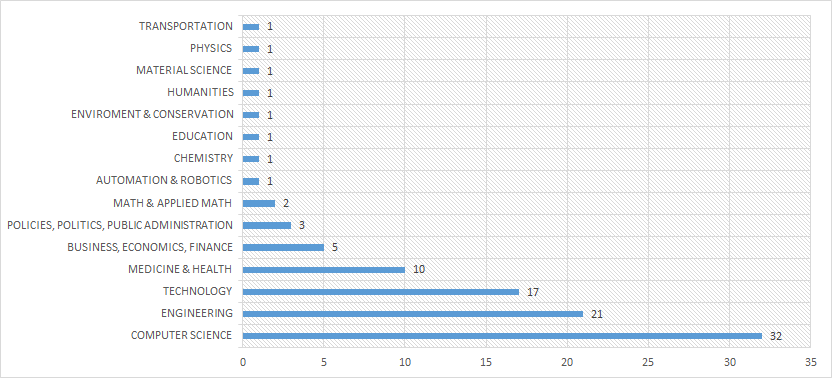
| Agenda Setting | Policy Design and Analysis | Policy Implementation | Policy Monitoring and Evaluation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture, Fisheries, Forestry & Foods | ||||
| Economy & Finance | ||||
| Education, Youth, Culture & Sport | ||||
| Employment & Social Security | ||||
| Environment & Energy | ||||
| Health | ||||
| Foreign Affairs and Defence | ||||
| Justice, Legal System & Public Safety | ||||
| Public Affairs | ||||
| Innovation, Science & Technology | ||||
| Urban Planning & Transport | ||||
| Institutional Questions / Internal Affairs |
You are free to download the data of this Knowledge base.
To do this you must be an authenticated user: log in or sign in now.
All the data are licensed as Creative Common CC-BY 4.0.